Motion on Rough Inclined Plane
Motion on Rough Inclined Plane: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Friction on Inclined Plane, Friction Due to Inclined Plane in Upward Motion, Friction Due to Inclined Plane in Downward Motion & Motion of Blocks on Moving Rough Incline Plane etc.
Important Questions on Motion on Rough Inclined Plane
Starting from rest, a body slides down a inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide down the same distance in the absence of friction. The coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane is
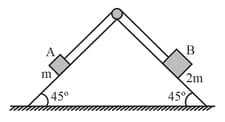
Block of mass and block of mass are placed on a fixed triangular wedge by means of a massless inextensible string and a frictionless pulley as shown in figure. The wedge is inclined at to the horizontal on both sides. The coefficient of friction between block and the wedge is and that between block and the wedge is . If the system of and is released from rest, find the acceleration of .
The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough. A body starting from rest at the top will again come to rest at the bottom if the coefficient of friction for the lower half is
Blocks and shown in the figure are connected with a bar of negligible weight. and each has mass , the coefficient of friction between and the plane is and that between and the plane is. What is the total force of friction between the blocks and the plane
A body slides down an inclined plane of inclination . The coefficient of friction down the plane varies in direct proportion to the distance moved down the plane . The body will move down the plane with
A body is moving down a long inclined plane of in . The coefficient of kinetic friction between the body and the plane varies as where is the distance moved down the plane. The body will have its maximum velocity when it reaches:
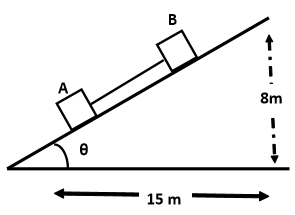
In the figure shown, if friction coefficient of blocks and with an inclined plane is and , respectively, then find the correct statement.
A block of base and height is kept on an inclined plane. The coefficient of friction between them is . The inclination of this inclined plane from the horizontal plane is gradually increased from . Then
The minimum force required to start pushing a body up a rough (frictional coefficient ) inclined plane is while the minimum force needed to prevent it from sliding down, is If the inclined plane makes an angle with the horizontal such that , then the ratio is
A small block slides without friction down on a inclined plane starting from rest . Let be the distance travelled from time to . Then is
A box is kept on an inclined plane making an angle from the horizontal and coefficient of friction . If is the minimum force required to start pushing it above the plane and to prevent it from sliding. Find the ratio if .
A box of mass rests upon an inclined plane. The inclination of the plane to the horizontal direction is gradually increased. It is found that when the slope of the plane is in , the box starts sliding down the plane. Find the co-efficient of friction between the box and the plane. What force applied to the box parallel to the plane will make it move up the plane ? .
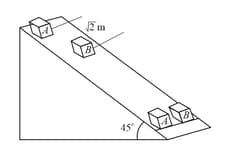
Two blocks and of equal masses are released from an inclined plane of inclination at . Both the blocks are initially at rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the inclined plane is while it is for block . Initially the block is behind the block . At what time in seconds will their front faces come in a line, (Take )
A block of mass is placed on a rough plane with coefficient of friction whose angle of inclination with the horizontal can be varied slowly as . If the block is tied with an elastic string of stiffness and be the instantaneous deformation in the string, then the correct variation of versus is given by
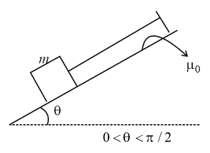
particle of mass carrying charge of is able to remain at rest on rough inclined plane of inclination when a uniform horizontal electric field of is applied. Coefficient of friction is (Acceleration due to gravity )
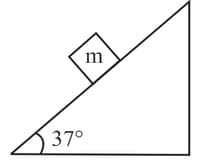
A block of mass rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is The frictional force on the block is
(Assume )
A block of mass is sliding down on a rough fixed inclined plane having coefficient of friction as shown in the figure. The acceleration of the block is (Take
The upper half of an inclined plane of inclination is perfectly smooth while lower half is rough. A block starting from rest at the top of the plane will again come to rest at the bottom, if the coefficient of friction between the block and lower half of the plane is given by
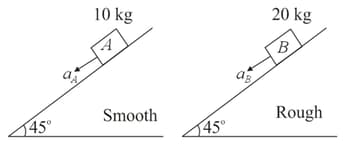
The ratio of acceleration of blocks placed on smooth incline with block placed on rough incline is . The coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline is :
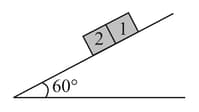
A block slides down an inclined plane with an acceleration as shown in fig. Then coefficient of kinetic friction is :-